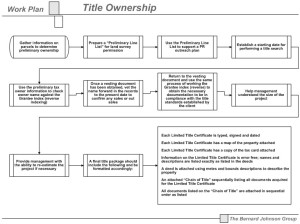
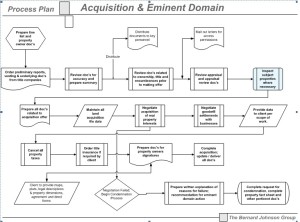
Process
Project Management Methodology
The need to successfully perform client project work to a high level of quality assurance and to attain the correct balance between the traditional project triad of scope, cost and schedule requires a comprehensive project management approach and detailed work plans. Key members of the project management team with experience and expertise on both large and small, complex multidisciplinary projects develop a project management plan to ensure that all project goals, milestones and deliverables are successfully achieved, and within the scheduled time frame.
A Project Management Plan typically involves:
- Analysis and design of objectives and events
- Project scheduling
- Action item “punch list”
- Project work plan
- Data reporting and management plan
- Planning work according to the objectives
- Assessing and controlling risk
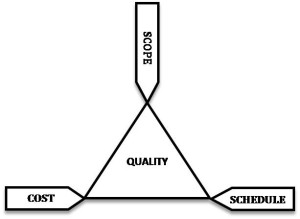
- Estimating required resources
- Allocating resources
- Organizing the work
- Assigning tasks
- Directing the activities
- Change control
- Tracking and reporting progress
- Quality management
- Issues management
- Defect prevention and rectification
- Project Closure
- Communicating with stakeholders
Several basic approaches to project management are the “traditional” phased approach and the critical chain approach. However, today’s business environment, where projects range from small & simple to large & complex, necessitates a flexible Project Management approach, determined on a project by project basis. Large and complex Project Management plans often times prove cumbersome on smaller projects, hence the Bernard Johnson Group’s use of differing project management approaches tailored to the specific project at hand.
Alternate PM approaches for smaller projects are “light weight” models that allow for more flexibility and adaptability during the life of the project.
Regardless of the methodology used, the project development process will have the same major stages: initiation, planning/development, execution, maintenance & control, and project closure.
The project manager’s roll is to ensure that work progresses on schedule; maintain communication between the client and contractor to minimize the risk of failure; achieve completion of the project within budgetary / time constraints; and facilitate communication between all the stake holders and team members. In tandem with the client the project manager develops the project schedule with critical path items, benchmarks, project deliverables and a realistic completion schedule.
The project manager monitors and manages personnel time, equipment and materials to ensure targeted cost control throughout the life of the project, timely and thorough completion of the work, coordination among team member activities, and directs the project close-out, ensuring quality deliverables as defined by the original scope of work.